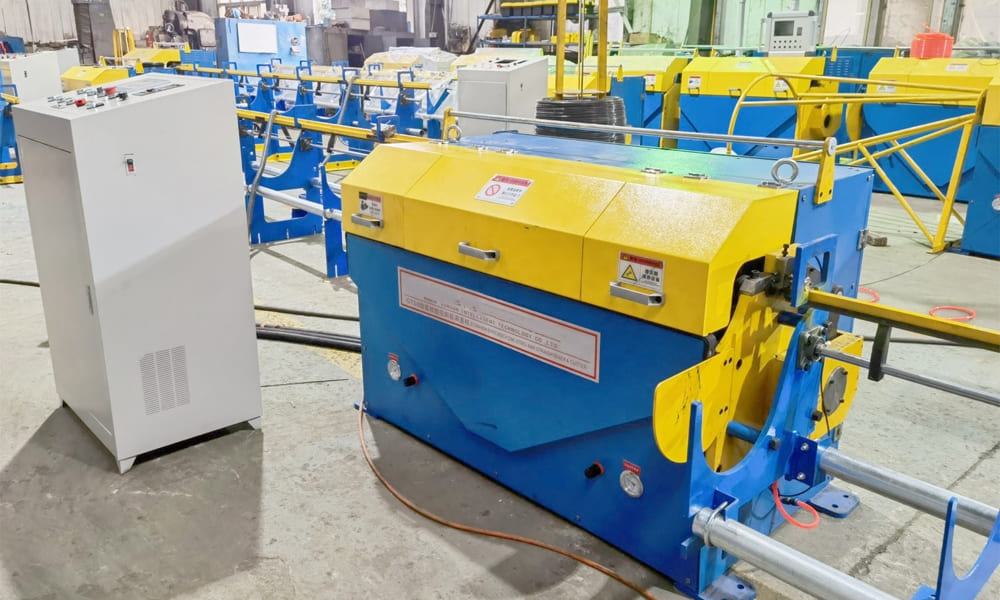
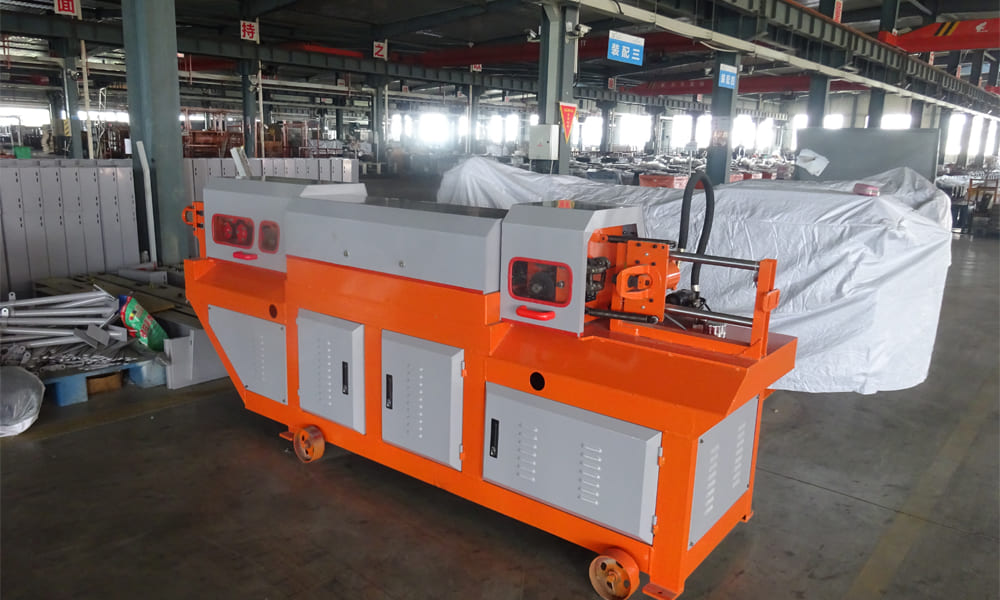
Steel wire straightening and cutting machine, typically designed for wire diameters of less than 12mm, are essential in construction projects. Steel mills often roll these bars into rings for easy transportation and to prevent deformation. However, these rolled bars require secondary processing, such as straightening and shearing, on-site. Traditional straightening methods can lead to problems like weight and size deviations, poor straightness, and compromised mechanical properties, which ultimately affect construction quality and efficiency.
The Need for Advanced Processing Equipment
As construction projects grow larger, the demand for high-quality steel bars increases. Traditional methods often fall short due to their slow speed and low accuracy. Modern engineering standards require precise steel bar processing, leading to the development of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) steel bar straightening and cutting machines, which are now indispensable in the industry.
Key Features of CNC Steel Wire Straightening and Cutting Machine
CNC steel bar straightening and cutting machines are sophisticated systems designed to efficiently straighten, size, and shear wire rod steel bars. These machines consist of several key components:
- Steel Bar Pay-off Frame: Holds the rolled wire rods.
- Wire Management Frame: Guides the wire rods into the straightening process.
- Straightening Host: The main component where the straightening occurs.
- Material Receiving Frame: Collects the straightened and cut bars.
These machines operate in a high-speed, automated flow-line manner, greatly enhancing production efficiency.
Straightening Method
CNC machines use two primary methods for straightening steel bars:
- Rotary Straightening with a Hub:
- Utilizes high-speed rotation and staggered straightening blocks.
- Bends the wire multiple times to achieve straightness.
- Offers good speed and straightness but may damage the surface of the bar.
- Parallel Roller Straightening:
- Employs two rows of interlaced multi-wheel rollers.
- Directly deforms and straightens the steel bars.
- While slightly slower, it preserves the integrity of the steel bar surface.
Advantages of CNC Machine
- High Precision and Efficiency:
- Controlled by high-precision servo motors and encoders, with length errors generally within ±3mm.
- Rotary equipment features a flying shear mechanism for continuous cutting without stopping.
- Roller machines have active lower wheels with internal gear and synchronous belt transmission, ensuring better accuracy and speed.
- Automation and Intelligence:
- Equipped with user-friendly touch screens for human-computer interaction.
- Tasks can be manually input or assigned through a control center.
- Automatic operations and task status updates enhance convenience and efficiency.
Safety Operating Procedure
To ensure safe and efficient operation of CNC steel bar straightening and cutting machines, follow these guidelines:
- Pre-Work Checks:
- Tighten all connecting bolts and ensure proper lubrication.
- Remove any foreign objects from the machine.
- Firmly install all safety guards and protective devices.
- Machine Setup:
- Smoothly install the straightening machine.
- Align the material rack, trough, straightening guide cylinder, and cutting knife hole.
- Ensure the motor has proper connections and leakage protection.
- Operational Checks:
- Test the machine at idle speed.
- Adjust gaps, tighten bolts, and fill oil levels as needed.
- Begin work only after confirming normal operation.
- During Operation:
- Stop immediately if any abnormal conditions or noises occur.
- Select appropriate straightening blocks and transmission speeds based on the steel bar diameter.
- Ensure all protective parts are covered, and straightening blocks are securely fixed before feeding.
- Cut off non-straight ends of steel bars before feeding them into the machine.
- Feeding and Straightening:
- Use a 1m steel pipe to guide the steel bar into the machine.
- Maintain a safe distance between hands and the pull wheel.
- Gradually adjust straightening blocks if bars remain bent after the initial straightening.
- Length and Accuracy Checks:
- Stop the machine to check the length of cut bars.
- Adjust the limit switch or fixed length plate if necessary.
- Material Handling:
- Ensure round steel bars are securely placed on the ring frame.
- Stop the machine if wires become tangled or bars come off the frame.
- Position the wire rod rack 5 to 8 meters from the machine at an appropriate height.
- Travel Switch Cam:
- Adjust the cam to move freely and center it in the bearing frame.
- Prevent continuous cutting by ensuring the cam is not stuck.
- Safety Around the Machine:
- Keep non-operational personnel away from the machine.
- Exercise caution when the material plate is nearly empty to avoid injuries from the ends of the steel bars.
Conclusion
CNC steel wire straightening and cutting machine represent a significant advancement in construction technology. These machines enhance processing speed and accuracy while ensuring that the quality of steel bars meets modern construction standards. By following proper safety procedures, construction sites can improve efficiency and safety in steel bar processing.