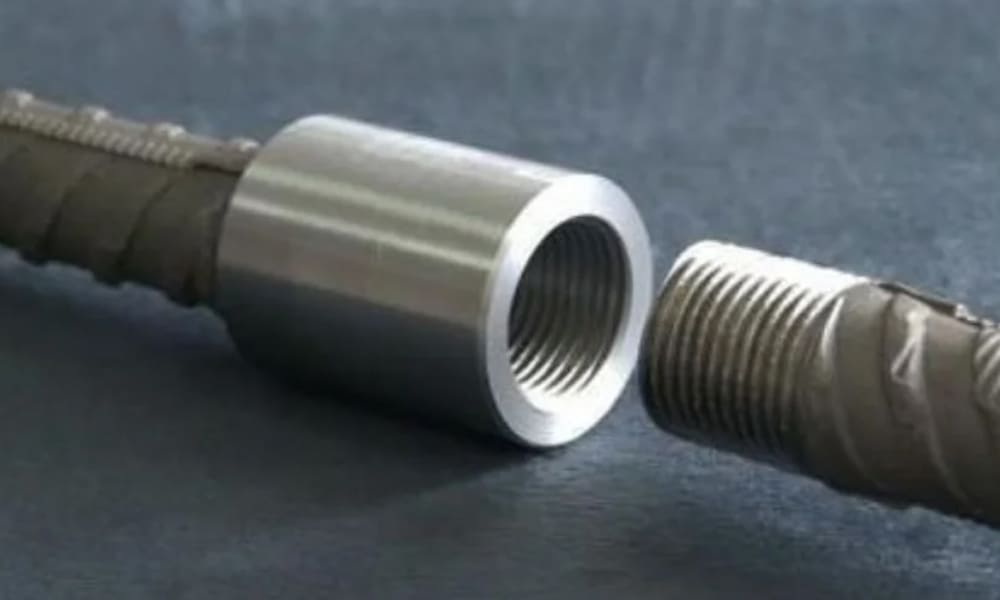
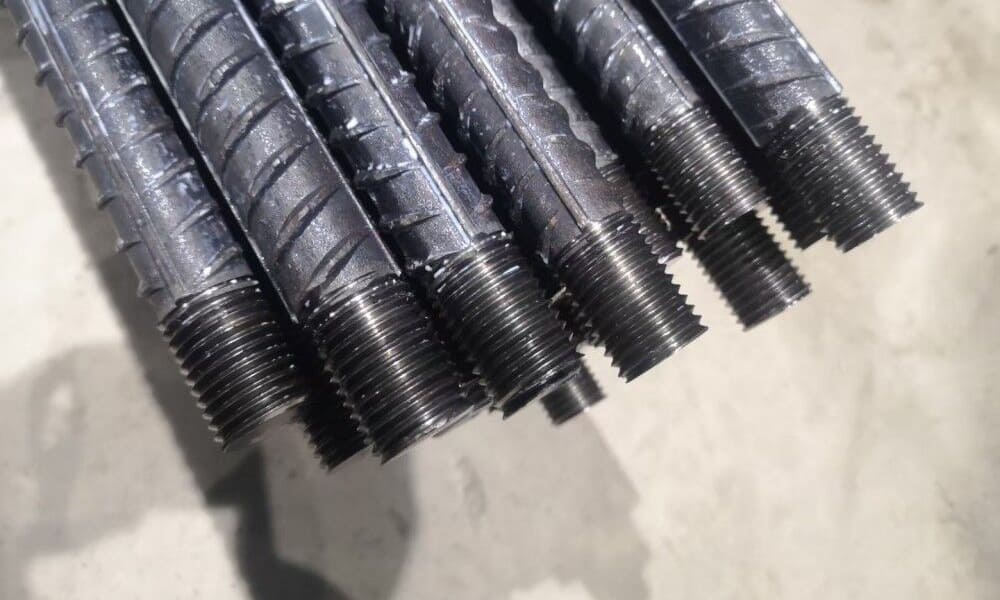
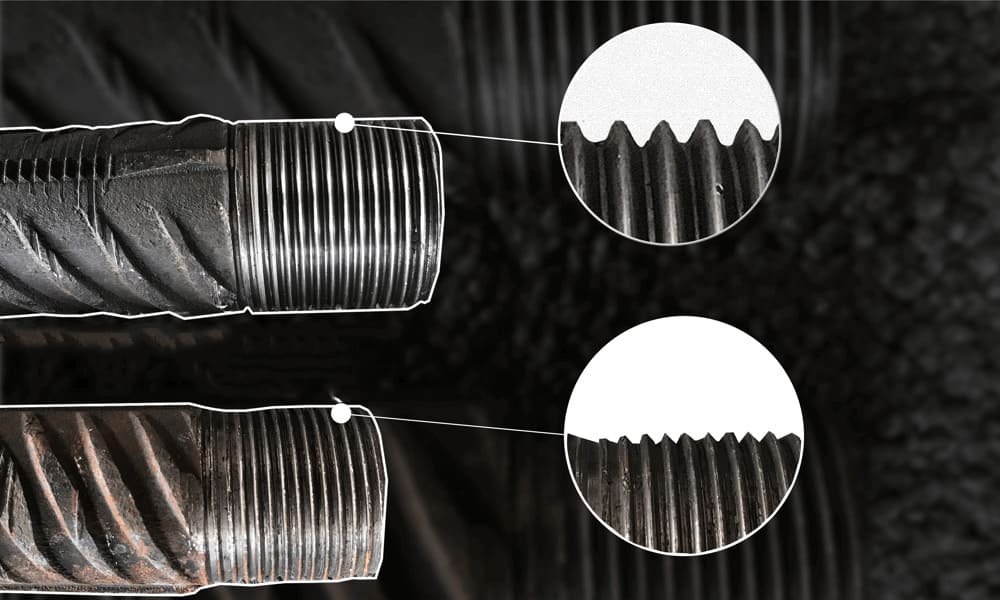
Steel bar connection play a vital role in modern construction by providing secure and reliable methods for connecting steel bars. They are particularly important in earthquake-resistant and non-seismic concrete structures. Below, we explore six common types of steel bar connection, their applications, and their advantages.
1. Standard Connection
Application: Standard connections are versatile and suitable for all types of concrete structures that require high strength and ductility. They effectively connect steel bars of varying diameters and are useful for joining bent steel bars, extra-long horizontal bars, and fixed steel bars.
Features:
-
- Connects thick and differently sized steel bars.
- Effective for intersecting steel columns and beams.
- Ideal for butt joints in steel cages and fixed bars.
2. Flared Connection
Application: Flared connections are designed for situations where aligning steel bars with the connection sleeve is challenging, commonly used in columns with thick vertical steel bars.
Features:
-
- Facilitates connections in tight spaces.
- Maintains the same quality control and connection method as standard joints.
3. Positive and Negative Thread Connection
Application: This connection type is ideal when steel bars cannot rotate and require internal force adjustments, such as in construction joints and post-casting strips.
Features:
-
- The sleeve features both positive and negative threads, allowing it to loosen or tighten steel bars in one direction.
- Enables efficient internal force adjustments.
4. Reducer Connection
Application: Reducer connections join steel bars of different diameters, making them suitable for reinforced concrete structures subjected to bidirectional tension and compression forces.
Features:
-
- Connects HRB335 and HRB400 grade steel bars of varying diameters.
- Applicable for horizontal, vertical, and oblique directions.
5. Extended Connection
Application: Extended connections are used when steel bars are too long or densely packed, making rotation difficult. The sleeve is pre-screwed into an extended thread on one bar and then connected to another.
Features:
-
- Facilitates easy connections by rotating the steel bar half to one turn.
- Compatible with standard connecting sleeves.
6. Locking Female Connection
Application: This type is ideal for steel bars that cannot rotate, such as bent bars and docked steel cages in bridges and cast-in-place piles.
Features:
-
- Involves pre-screwing a lock nut and connecting sleeve into an extended thread.
- The sleeve is then screwed into another steel bar end and secured with a nut.
- Provides high mechanical strength and reliable connections.
Advantages of Steel Bar Connection
- Superior Mechanical Properties: Steel sleeve connections enhance the strength of the thread and steel bar by rolling the ends and cold-working the material. This compensates for any strength loss due to thread diameter reduction, ensuring joint strength exceeds that of the parent material.
- Convenience and Efficiency: These connections can be easily operated in confined spaces with densely packed steel bars. The prefabrication of sleeves ensures consistent quality, while on-site rolling equipment can process numerous joints quickly, making them ideal for large projects.
- Environmental Benefits: The construction process for steel sleeve connections is safe and environmentally friendly, avoiding pollution and open flames. This allows for continuous construction without time-of-day restrictions.
Conclusion
Steel sleeve connections offer a variety of solutions for different construction scenarios, providing reliable and efficient methods for joining steel bars. From standard and flared connections to positive and negative thread, reducer, extended, and locking female connections, each type has specific applications and advantages that contribute to the strength and integrity of modern concrete structures.